Services
Nipple Reduction
Nipple Reduction
.jpg)
Surgery Features
The nipple is considered the most important part of the breast tissues as far as function goes. Despite its lightweight content in the breast tissues, dozens of breast ducts are concentrated in the nipple region, secreting milk through the infant’s sucking and achieving the purpose of feeding through the milk secreted by the mammary glands. Therefore, it is the most important part that brings out the feeding function of the breasts. It is also a highly sensitive area; therefore, sightly nipple appearance complements the beauty of enhanced breasts.
♦The Golden Ratio.jpg)
Generally speaking, nipples that are too large, small, inverted, elongated, out of shape, or in the wrong direction (e.g. Facing downwards) are less than ideal shapes. What should an ideal nipple look like? An ideal nipple should have a diameter of about 0.8-1.2cm and a height of 4-7mm. Of course, there are also many who are fond of small nipples as well, depending on personal discretion. However, it is not advisable to have nipples that are too small or too flat, because they will have an effect on the appearance, breastfeeding, and the sex partner as far as visual stimulus is concerned. Nevertheless, larger or darker nipples have little to do with sexual experience. Most likely than not, women who have breastfeeding experience tend to have proliferated or enlarged nipples due to excessively frequent stimulation, and thus the consideration for cosmetic surgery.
♦Who Need.jpg)
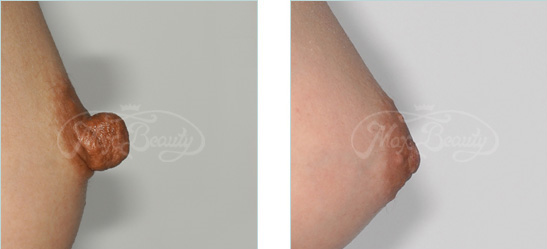
Although a nipple only comprises a small part of the breast tissues, it has its unique and irreplaceable physiological functions. Most mammary ducts are concentrated in the nipple tissues, although a very small number of mammary ducts are on the areola. Common breast development anomalies include: nipple hypertrophy, nipple inversion, and nipple nodular hyperplasia and papillary hyperplasia.
Surgical Approach
♦Nipple Hypertrophy.jpg)
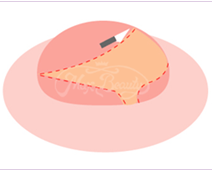
The nipple reduction surgery is adopted. The tissues nearby the mammary gland duct and appropriate nipple root are retained, while tissues between the two are completely removed and sutured. Some of the nerves and blood vessels are retained during surgery, not only to retain the sensations but also to make the appearance more beautiful.
 |
 |
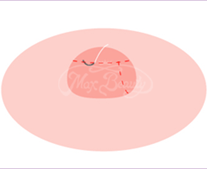 |
| Make an incision on redundant tissues but bypassing nerves. |
Carefully suture the incision to complete surgery. |
♦Nipple Inversion.jpg)
Nipple inversion may be caused by congenital or acquired factors. There are two causes of the formation: 1. The fibrous belt below the nipple is too tight, puling the nipple downwards; 2. There is inadequate tissue below the nipple, unable to support the nipple to give it the fullness it is supposed to have. This leads to concave external deformity. In addition to the abnormal external form, it is not conducive to infant sucking during breasted. Since the area is relatively inaccessible for women to clean, local eczema and even recurrent inflammation and infections may result.
♦Nipple inversion can be divided according to severity into Grade 1 (slight), Grade 2 (moderate), and Grade 3 (severe).jpg)
Grade 1 Nipple Inversion:
The nipple is located inside the areola, without depression or lateral grooves. It protrudes by itself in cold weather or with sexual stimulation. It maintains its projection fairly well most of the time, but occasion traction is noted. This degree of nipple inversion only requires frequent massage or squeezing to pull out the nipple.
Grade 2 Nipple Inversion:
The nipple is located within the nipple and areola, depressed with lateral grooves. Pinching still causes the nipple to pop out. In cold weather or with sexual stimulation, the nipple may protrude by itself. Most of the time, the nipple is inverted, but it can be pulled out or squeezed out, although it easily retracts back. If pulling or squeezing fails, surgical intervention may be needed.
Grade 3 Nipple Inversion:
Nipples are almost always inverted. With the kind of nipple inversion, surgical intervention is needed. By making an small incision through surgery, nipples can be pulled out and fixated, thus leading to substantial improvement results. Lactation and tactile functions remain unaffected in most cases.
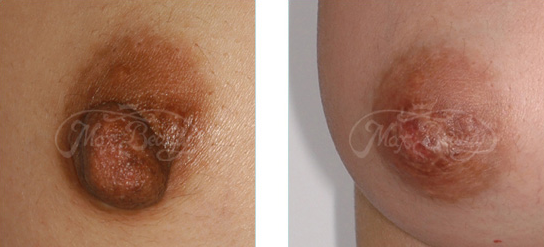
♦Protruding Nodular and Papillary Hyperplasia of Nipple.jpg)
These two symptoms can be reduced through various surgical procedures. Wounds are not easy to detect since they are hidden in the nipple or areola tissues. Local anesthesia can be applied for the above surgical procedure. General anesthesia may also be administered to simultaneously complete breast augmentation, breast reduction, or breast lift surgery.
Precautions
| 1.Please take postoperative anti-inflammatory medicine, four times a day, after three meals and before sleep to reduce swelling and prevent inflammation. |
| 2.Wound care: First, dip a cotton swab in saline solution and clean the wound with a dry swab. Apply ointment on the wound once in the morning and evening. Do not be in contact with raw water to avoid infection. |
| 3.Depending on personal conditions, suture is removed 10-14 days post operation. Contact with raw water to shampoo hair can only be done 24 hours after suture are removed. |
| 4.The occasion numbness of the nipple is normal, which will be gradually returned to normal after several weeks. |
| 5.During wound healing, avoid excitant foods (such as coffee, tea, tobacco, alcohol, spicy foods, diet pills, herbal medicine, etc.) and foods that are too hard. Take more high-protein foods (such as fish, meat, beans, eggs, milk) to promote wound healing. |
| 6.The postoperative swelling around the areola is a normal process, which subsides after about 5-7 days. Please have patience, as completely recovery may take up to 2-3 weeks or longer. |
Q&A
Q:Is the occasional temporary paralysis of the areola normal?
A:It is normal. It will gradually return to normal a few weeks later.
Q:How about anesthesia?
A:In general, only local anesthesia is required. Under special circumstances, local anesthesia with sedation may be adopted.
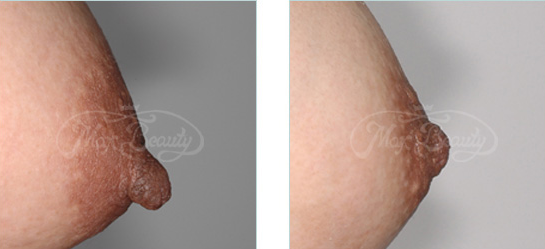
Case
♦Case
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|